Recently, the paper "Identity Guided Collaborative Learning for Cloth Changing Person Reidentification IGCL" written by Professor Gao Zan from our university has been accepted and published in the top international academic journal "IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligenc-e" (IEEE TPAMI) recognized in the fields of artificial intelligence, pattern recognition, computer vision, and machine learning. IEEE TPAMI ranks first among the four A-class journals in the field of artificial intelligence recognized by the Chinese Computer Society, and is the top journal in the fields of computer vision and pattern recognition, with an average impact factor of 26.7 over five years. According to the current popular Google Scholar Citation statistics, IEEE TPAMI ranks first on the H5 index with a score of 165 in all computer engineering, electronic engineering, and artificial intelligence related journal lists. It mainly collects original scientific research achievements in the fields of artificial intelligence, pattern recognition, computer vision, and machine learning, with an annual enrollment of only about 200 articles. It is one of the most important academic journals in the fields of artificial intelligence, pattern recognition, computer vision, and machine learning.
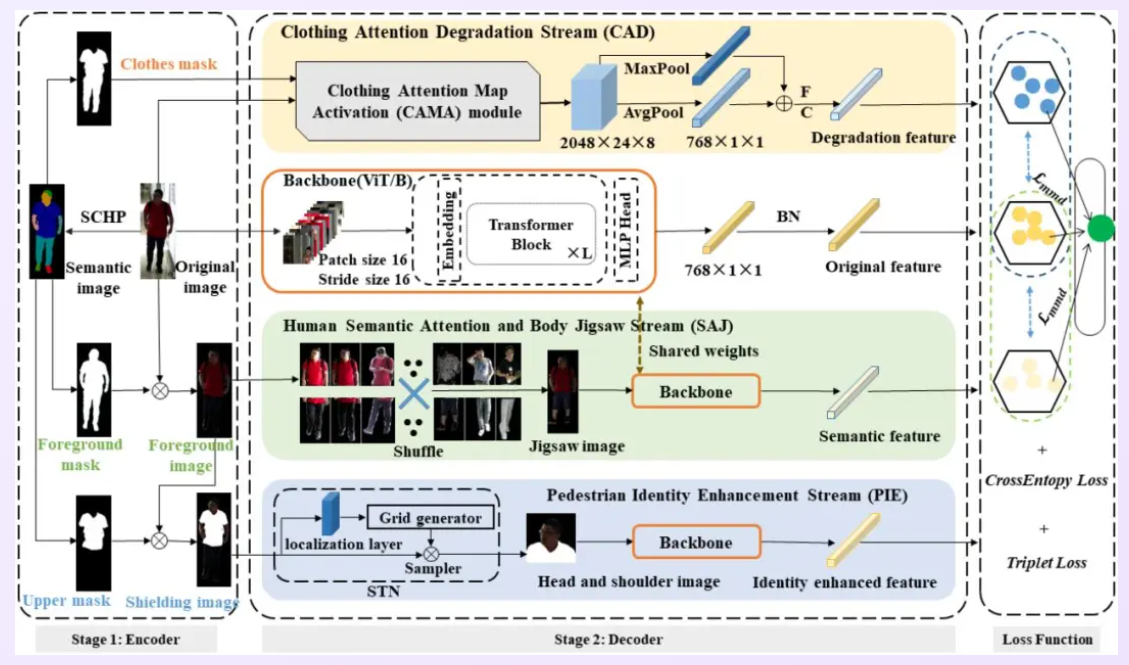
This study focuses on the scene of changing clothes in pedestrian re identification, explores the complex relationships between intra - and inter class changes of pedestrians, extracts pedestrian representations that are not easily affected by appearance changes, and conducts in-depth research. A new identity guided joint learning scheme, IGCL, is proposed. This scheme combines clothing attention degradation flow, human semantic attention and human puzzle flow, and pedestrian identity enhancement flow in an end-to-end unified framework for joint exploratory learning, effectively learning pedestrian identity identification features that are invariant to clothing changes. A large number of experimental results have shown the superiority of the proposed IGCL scheme, with extracted features having stronger representation and discrimination capabilities, and weaker correlation with interference information such as clothing.